閉口き裂に対する非線形超音波法
Nonlinear Ultrasonic Testing for Closed Cracks
通常の超音波法では,「音響インピーダンス」と呼ばれる「音の通りやすさ」が変化するところで超音波が反射する現象を利用します.
そのため,母材(部材の健全部)と欠陥(空洞,き裂,減肉,腐食部など)の音響インピーダンスが異なる場合は,発生した反射波を受信することで欠陥の有無やその位置を推定できます.
しかしながら,向かい合うき裂面が閉じていると,超音波がそのまま透過して反射波が得られない場合があります.
このような状況下では,き裂の見落としやき裂深さの過小評価が起きてしまうかもしれません.
そのため,
非線形超音波法と呼ばれる方法が閉じたき裂の検出や計測に期待されています.
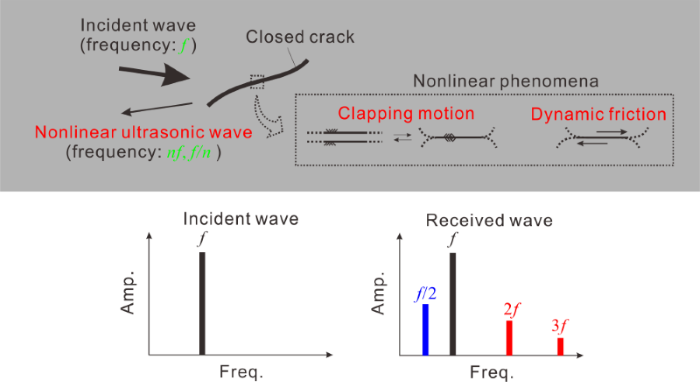
非線形超音波法では,大振幅(数nmから数十nm程度の変位)の超音波をき裂に入射することで,き裂面の接触を伴う振動を誘発して,その結果発生する非線形超音波と呼ばれる波を受信することで,き裂の検出や計測を目指します.
非線形超音波は高調波(入射周波数の整数倍)と分調波(入射周波数の整数分の一)から成るとされていて,それらの発生メカニズムの解明や定量的な評価を目指して数値シミュレーションを用いた研究を行っています.
The conventional ultrasonic method is based on the acoustic impedance mismatch, which causes ultrasonic waves to reflect when encountering a boundary between materials with different acoustic impedances.
Therefore, if the acoustic impedance of the base material (i.e., the healthy part of the member) and the defect (such as a cavity, crack, wall thinning, corroded area, etc.) are different, the location and size of the defect can be estimated by receiving the reflected waves.
However, if the crack surfaces facing each other are closed, the ultrasonic waves may pass through without scattering, and the reflected waves cannot be received.
In such circumstances, a crack may be missed or the crack depth may be underestimated.
Nonlinear ultrasonic testing is expected to address this issue by detecting and measuring closed cracks.
In nonlinear ultrasonic testing, a large-amplitude incident wave is directed into cracks, inducing vibrations of the crack faces with contact.
As a result, the received wave includes nonlinear ultrasonic waves, which consist of higher-harmonic and sub-harmonic wave components.
The higher-harmonic and sub-harmonic waves correspond to integer multiples and integer fractions of the incident frequency, respectively.
We investigate the generation mechanism and quantitatively evaluate these waves using numerical simulations.
T. Maruyama: Harmonic balance-boundary element and continuation methods for steady-state wave scattering by interior and surface-breaking cracks with contact acoustic nonlinearity, International Journal of Solids and Structures 210-211, pp.310-324 (2021).
ガイド波を用いた非破壊評価とモニタリング技術の開発
Technology Development of Nondestructive Evaluation & Monitoring using Guided Waves
(超)音波は板,棒,管のような長大構造物をガイド波として,長距離を低減衰で伝搬することが知られています.
そのため,ガイド波を用いれば,通常のP波とS波を用いた超音波探傷と比較して,遠距離からの検査やアクセス困難な位置の検査が可能になることが期待されます.
ガイド波は分散性と多重モード性という性質を持っていおり,導波路の形や材料によってその性質が変化します.
また,ガイド波の欠陥(空洞,き裂,減肉,腐食部など)での散乱現象は複雑で,複雑なモード変換が発生します.
これらの現象を的確に理解するために,数値シミュレーションを用いたアプローチがとても役立ちます.
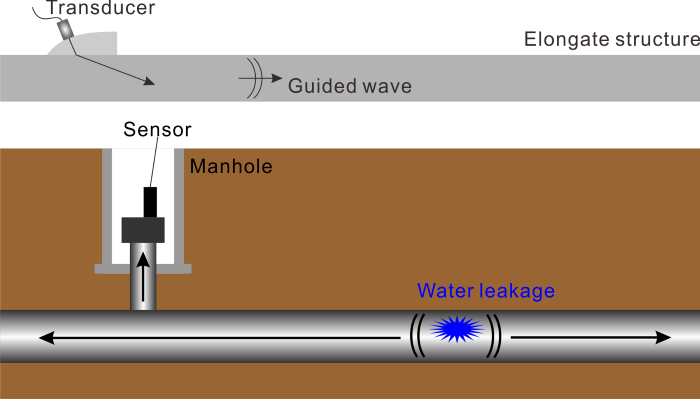
当研究室では,上水道管の漏水検査技術として漏水音を測る方法について研究しています.
管径や計測距離に対する既存技術の測定限界を広げて,大口径の上水道管をマンホール位置からモニタリングできる技術の開発を目指しています.
ガイド波の性質をうまく利用すれば,現在の測定限界を広げられるのではないかということに着目して研究を進めています.
(Ultra)sonic waves propagate over long distances with low attenuation as guided waves in elongate structures such as plates, rods, and pipes.
Therefore, guided waves are expected to allow inspection from long distances and in hard-to-access locations compared to conventional ultrasonic inspection techniques that use P and S waves.
Guided waves exhibit properties of dispersion and multi-modes, which depend on the shape and material of the waveguide.
Furthermore, scattering phenomena of guided waves due to defects (such as voids, cracks, thinning, and corrosion) are complex, and numerical approaches are helpful in understanding them.
In our laboratory, we are also studying the detection of water leakage in water supply pipes by measuring the (ultra)sound.
Our objective is to develop a technology that can monitor large-diameter pipes from manhole positions by expanding the measurement limits of the existing technologies.
For this purpose, we are focusing on the properties of guided waves in water supply pipes buried in the ground.